CURRENT ISSUE
October, 2025
No. 110 (10)
2024 Impact Factor: 7.9
2024 Journal Citation Indicator: 1.9
2024 CiteScore: 11.3
2024 Journal Citation Indicator: 1.9
2024 CiteScore: 11.3
EDITOR'S PICKS
Spotlight Review Article
Asciminib for Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemias
ARTICLES IN THREE SENTENCES
Article
A phase I/IIa trial of PXS-5505, a novel pan-lysyl oxidase inhibitor, in advanced myelofibrosis
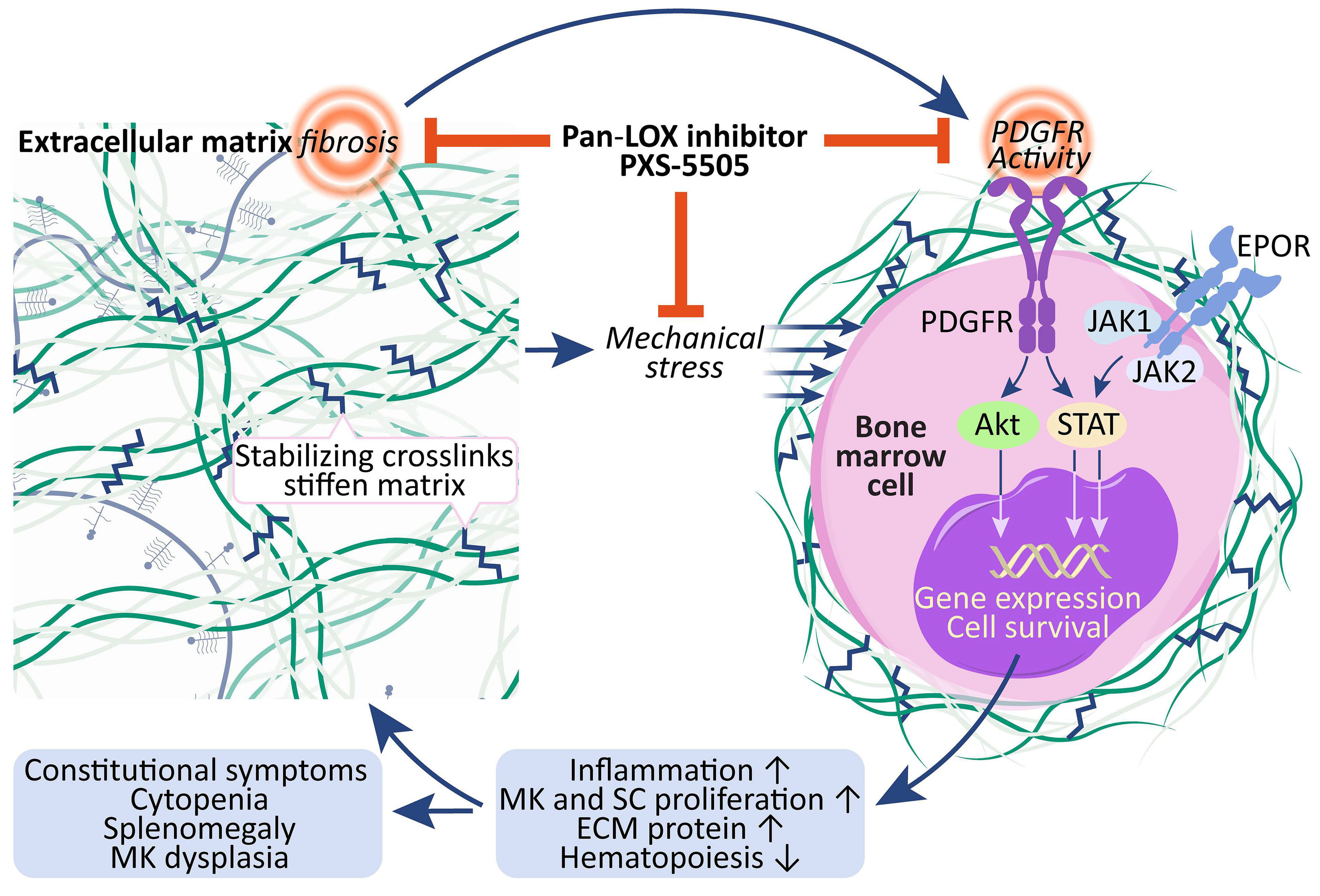
An antifibrotic therapy capable of normalizing the bone marrow (BM) microenvironment remains a significant gap in the current treatment landscape of myelofibrosis. Vacchani and colleagues present results of the PXS5505-MF-101 trial, a multicenter phase I/IIa study of PXS-5505, a novel pan-lysyl oxidase inhibitor, in myelofibrosis patients. Safety and tolerability data of PXS-5505 and preliminary indications of clinical efficacy, including a reduction in BM collagen, support continued investigation of PXS-5505.
Article
Production of platelets in vitro in functionalized 3-dimensional scaffolds mimicking the bone marrow niche
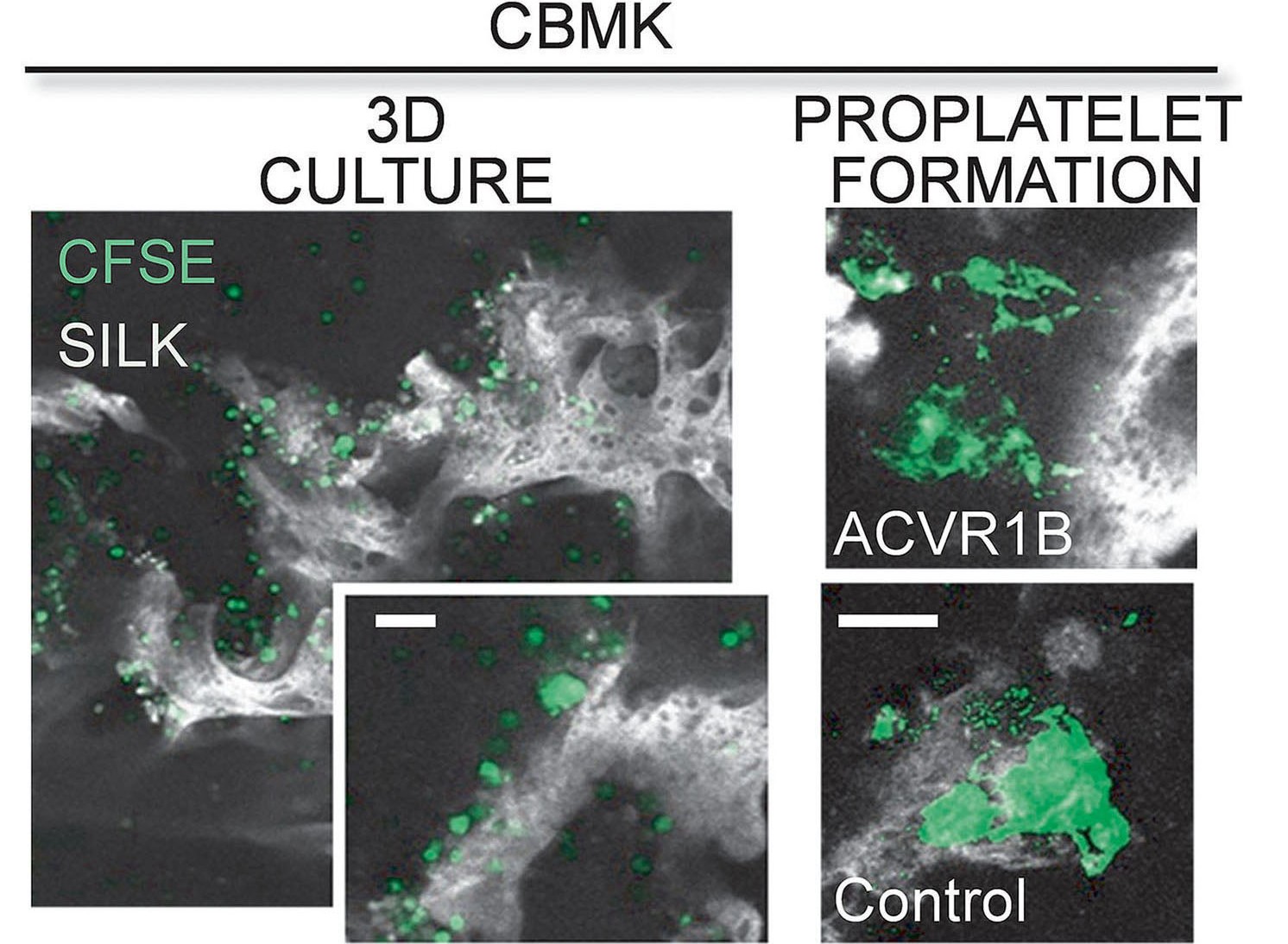
In vitro production of platelets could offer a viable alternative to donor-dependent products for transfusion. Foster and colleagues analyzed the proteomic profiles of several cell types that promote platelet production by cultured megakaryocytes in vitro to recreate the chemical and physical bone marrow niche and thereby enhance platelet production. They identified novel proteins whose role in platelet formation was previously unknown and highlighted the potential gain of recreating the megakaryocyte niche to allow in vitro platelets to become a viable alternative for transfusion.
Letter
The specific transcriptional profile and clonal selection of monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significancelike behavior predict an exceptionally favorable prognosis in multiple myeloma
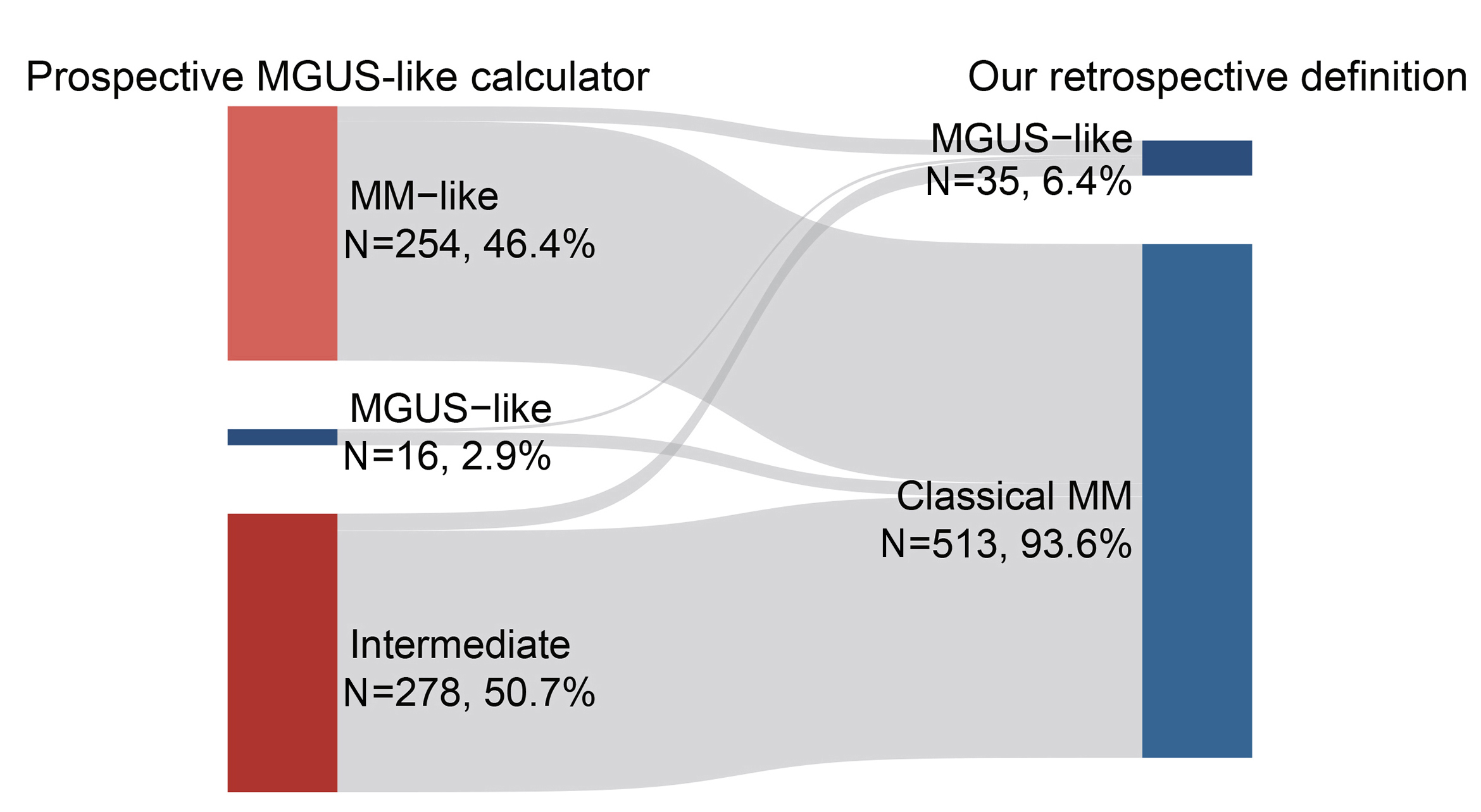
Some myeloma patients achieve unexpectedly long-term progression-free survival (PFS) despite failure to achieve complete response after systematic treatment, displaying a stable clinical course similar to that of patients with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS). Yan and colleagues analyzed clinical, transcriptomic, and genomic aspects of a retrospective cohort to illuminate the underlying causes contributing to the distinctive MGUS-like clinical behavior.
Article
Truncated form of human CD19 antigen as a suicide gene to control T-cell alloreactivity: ΔCD19
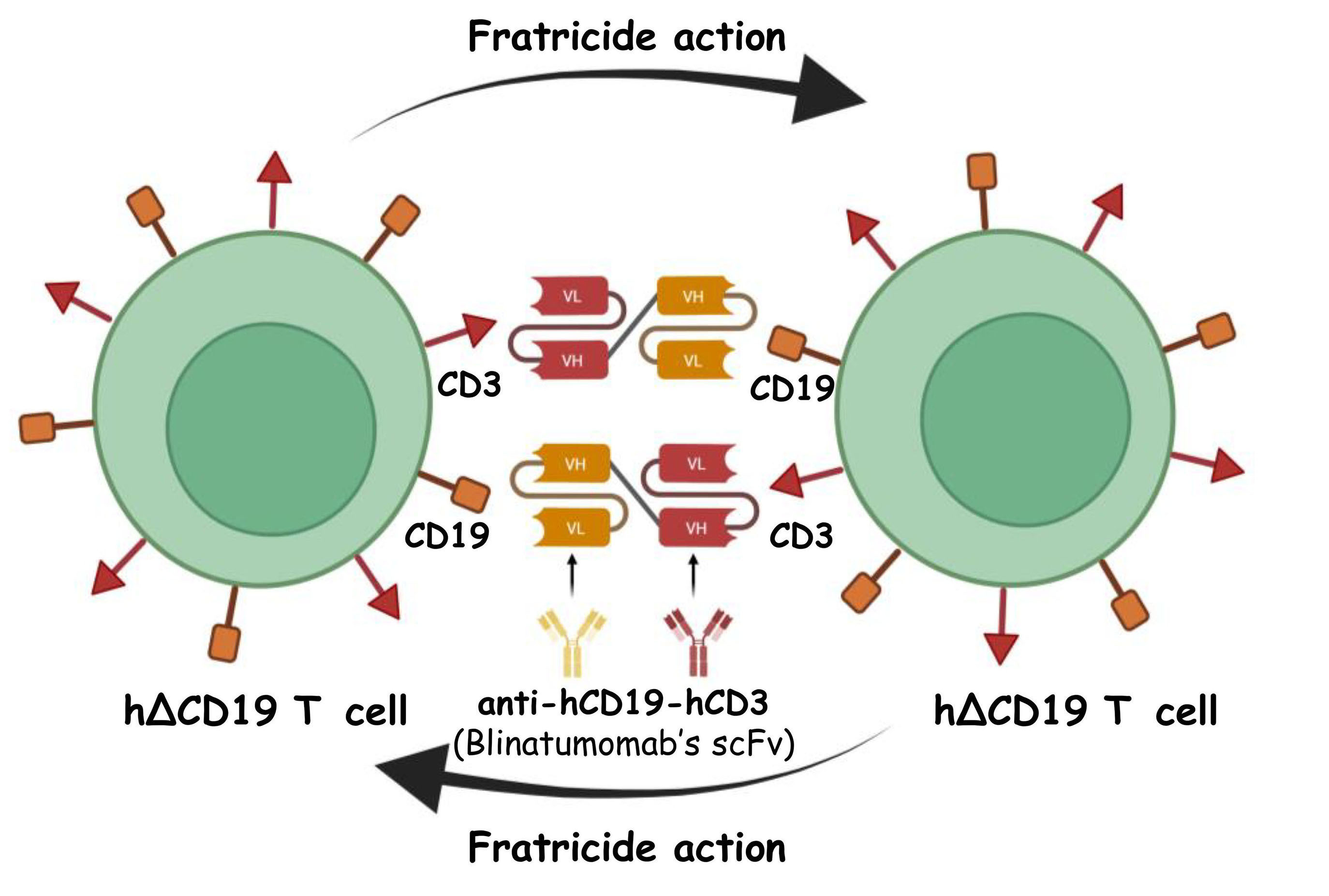
New approaches able to prevent graft-versus-host disease and maintain the graft-versus-leukemia effect with donor lymphocyte infusions in patients relapsed after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation are needed. Manni and colleagues developed a preclinical strategy based on the use of ∆CD19, a new suicide gene, which can be targeted using an anti-hCD19-hCD3 T-cell bispecific T-cell engager molecule. They demonstrated prompt elimination of the most alloreactive ∆CD19 T cells, and the preservation of non-activated/non-alloreactive T cells.
TAKE ADVANTAGE FROM HAEMATOLOGICA





